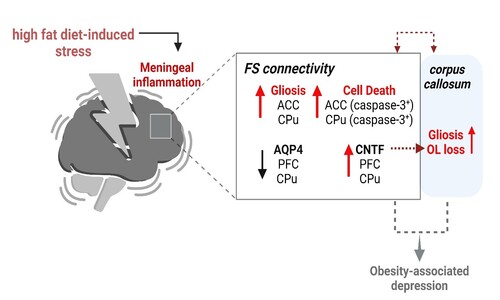
長期攝取高脂飲食誘發額葉–紋狀體迴路和胼胝體的神經發炎
高脂飲食(high-fat diet)引發的肥胖會誘導中樞與周邊的發炎反應,伴隨星狀膠細胞 (Astrocytes) 和微膠細胞 (Microglia)的活化–神經膠細胞增生(gliosis)。臨床證據顯示,肥胖與憂鬱症相關;額葉-紋狀體迴路 (frontal-striatal connectivity;FS)亦與壓力性憂鬱症相關,此迴路涵蓋的腦區包含前額葉皮質(PFC)的前扣帶迴(ACC)與背側紋狀體尾狀核(CPu)。本篇文章研究慢性肥胖是否在這些腦區引發神經發炎反應。結果顯示,肥胖小鼠的腦膜淋巴系統(glymphatic system)出現免疫細胞聚集,並觀察到神經膠細胞增生和胼胝體(corpus callosum)膠細胞活化,伴隨髓鞘和寡突膠細胞(oligodendrocyte;OL)的減少。此外,在慢性發炎的病理條件下,前額葉皮質和尾狀核的水通道蛋白4 (AQP4) 表達減少,而作為細胞因子的CNTF基因表達上升,可能促使神經損傷並干擾腦部淋巴系統的正常功能。
(https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jnc.16236)
Jing-Ting Fu (傅敬婷), Hui-Ting Huang (黃暉廷), Pei-Chun Chen, Yu-Min Kuo, Po-See Chen, Shun-Fen Tzeng (曾淑芬). Exploring the reduction in aquaporin-4 and increased expression of ciliary neurotrophic factor with the frontal–striatal gliosis induced by chronic high-fat dietary stress. Journal of Neurochemistry. 2024 Oct 7. doi: 10.1111/jnc.16236. Online ahead of print. (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39374168/)